AI-Powered Threat Detection: 20% Cost Savings in US Incident Response by 2025
AI-powered threat detection is transforming US cybersecurity by identifying hidden anomalies, projected to save organisations 20% on incident response costs by 2025 through enhanced prevention and faster resolution.
The digital landscape is evolving at an unprecedented pace, and with it, the sophistication of cyber threats. In this environment, AI-Powered Threat Detection: Uncovering Hidden Anomalies in US Networks to Save 20% on Incident Response in 2025 (FINANCIAL IMPACT) is not just a technological advancement but a strategic imperative. This article explores how artificial intelligence is reshaping cybersecurity, offering a proactive defense against malicious activities and delivering tangible financial benefits for organisations across the United States.
The Rising Tide of Cyber Threats in US Networks
The sheer volume and complexity of cyberattacks targeting US networks have reached critical levels. Traditional security measures, while foundational, often struggle to keep pace with polymorphic malware, zero-day exploits, and sophisticated phishing campaigns. The financial and reputational costs associated with successful breaches are staggering, prompting an urgent need for more intelligent and adaptive defense mechanisms.
Organisations face constant pressure to protect sensitive data, maintain operational continuity, and comply with an ever-expanding array of regulations. The human element, despite training, remains a significant vulnerability, and the sheer volume of alerts generated by security information and event management (SIEM) systems can lead to alert fatigue, allowing genuine threats to slip through the cracks.
Understanding the Current Threat Landscape
- Sophisticated Ransomware: Attacks are becoming more targeted and disruptive, often encrypting critical systems and demanding hefty ransoms.
- Supply Chain Attacks: Compromising a single vendor can provide access to numerous client networks, amplifying the impact of a breach.
- Insider Threats: Malicious or negligent insiders pose a persistent risk, often bypassing external defenses.
- IoT Vulnerabilities: The proliferation of interconnected devices expands the attack surface significantly, creating new entry points for adversaries.
These challenges underscore the limitations of purely signature-based detection systems, which are inherently reactive. The future of cybersecurity demands a shift towards predictive and proactive strategies, where anomalies are identified and neutralised before they can escalate into full-blown incidents.
The current threat landscape necessitates a paradigm shift in how US networks approach security. Relying solely on historical data and known attack patterns is no longer sufficient; a more dynamic and intelligent approach is required to safeguard critical infrastructure and sensitive information from the relentless onslaught of cyber adversaries.
AI’s Transformative Role in Anomaly Detection
Artificial intelligence is not merely an incremental improvement; it represents a fundamental shift in how we detect and respond to cyber threats. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, AI systems can analyse vast datasets from network traffic, system logs, and user behaviour to establish baselines of normal activity. Any deviation from these baselines, however subtle, can then be flagged as a potential anomaly, often indicative of a nascent cyberattack.
Unlike human analysts, AI can process and correlate information across disparate systems at machine speed, identifying patterns that would be invisible to the human eye. This capability is particularly crucial in detecting advanced persistent threats (APTs) that often employ stealthy tactics to evade traditional security controls over extended periods.
How AI Identifies Hidden Threats
AI algorithms are trained on enormous volumes of data, learning to distinguish between legitimate network activity and malicious behaviour. This training allows them to adapt to new threats without explicit programming for every new attack signature. The process involves several key steps.
- Data Ingestion and Normalisation: Collecting data from all relevant sources, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, endpoints, and cloud environments.
- Baseline Creation: Building a comprehensive profile of ‘normal’ network and user behaviour over time, accounting for typical fluctuations and patterns.
- Pattern Recognition: Utilising machine learning models (e.g., neural networks, support vector machines) to identify deviations from established baselines.
- Threat Scoring and Prioritisation: Assigning a risk score to detected anomalies, helping security teams focus on the most critical threats first.
This proactive anomaly detection capability significantly reduces the dwell time of attackers within a network, limiting the potential damage and subsequent incident response costs. The ability of AI to learn and evolve makes it an indispensable tool in the continuous battle against cybercrime.
By automating the detection of subtle indicators of compromise, AI empowers security teams to move from a reactive posture to a more predictive and preventive one, fundamentally changing the dynamics of cybersecurity defense within US networks.
Quantifying the Financial Impact: A 20% Saving by 2025
The promise of AI-powered threat detection extends beyond enhanced security; it offers tangible financial benefits, with projections indicating a potential 20% saving on incident response costs by 2025 for US organisations. These savings stem from several key areas, including reduced breach costs, optimised security operations, and improved business continuity.
Incident response is an expensive undertaking, encompassing forensic investigations, containment efforts, data recovery, legal fees, regulatory fines, and reputational damage. By detecting threats earlier and with greater accuracy, AI minimises the scope and impact of breaches, directly translating into significant cost reductions.
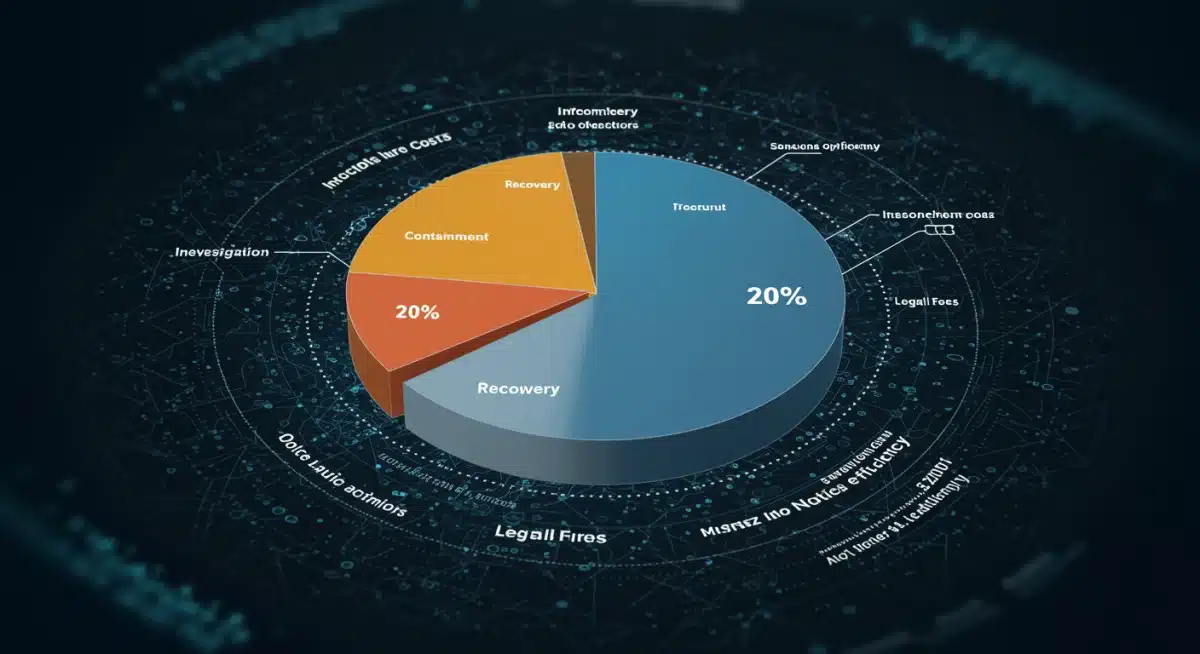

Mechanisms for Cost Reduction
AI contributes to financial savings through various direct and indirect mechanisms. These efficiencies are not merely theoretical but are being demonstrated in real-world deployments across diverse industries.
- Reduced Dwell Time: Faster detection means attackers spend less time in the network, limiting data exfiltration and system damage, thus lowering recovery costs.
- Automated Triage and Response: AI can automate the initial stages of incident response, such as alert correlation and even some containment actions, reducing the need for manual intervention and freeing up security analysts for more complex tasks.
- Fewer False Positives: By accurately distinguishing between genuine threats and benign anomalies, AI reduces the time and resources wasted on investigating false alarms.
- Improved Compliance: Proactive threat detection helps organisations avoid costly regulatory fines and legal disputes arising from data breaches.
- Enhanced Business Continuity: Minimising downtime due to cyber incidents ensures continuous operations, preventing revenue loss and maintaining customer trust.
The 20% saving projection is a conservative estimate based on the increasing maturity of AI technologies and their proven effectiveness in reducing the financial fallout from cyberattacks. This makes AI not just a security investment but a sound financial one.
Organisations that embrace AI-powered threat detection are not only bolstering their defenses but also strategically positioning themselves to mitigate the escalating financial burden of cybersecurity incidents, leading to significant savings in the coming years.
Implementing AI in US Network Security Infrastructures
Successfully integrating AI into existing US network security infrastructures requires careful planning, strategic investment, and a clear understanding of both the opportunities and challenges. It’s not simply about deploying a new tool; it’s about evolving an entire security posture to be more intelligent and adaptive.
Many organisations are starting with AI-driven Security Operations Centre (SOC) augmentation, where AI tools assist human analysts in sifting through vast amounts of data and prioritising alerts. This hybrid approach allows for a gradual transition while still reaping immediate benefits.
Key Considerations for Deployment
The journey to an AI-powered security infrastructure involves several critical steps and considerations. Addressing these proactively can ensure a smoother and more effective implementation.
- Data Quality and Quantity: AI models are only as good as the data they’re trained on. Ensuring clean, comprehensive, and relevant data feeds is paramount.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Seamless integration with SIEM, EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response), and other security tools is essential for a unified defense.
- Skill Gap: While AI automates many tasks, it also requires security professionals with expertise in AI, machine learning, and data science to manage and optimise these systems.
- Ethical AI Use: Addressing concerns around privacy, bias, and transparency in AI algorithms is crucial for maintaining trust and compliance.
- Continuous Learning and Adaptation: AI models need to be continuously updated and retrained to adapt to new attack vectors and evolving network environments.
Organisations should consider starting with pilot programmes to test AI solutions in specific areas before a broader rollout. This allows for fine-tuning and demonstrating value before a full-scale commitment.
The successful implementation of AI in US network security infrastructures will hinge on a holistic approach that combines advanced technology with skilled personnel and well-defined processes, ensuring maximum effectiveness and return on investment.
Overcoming Challenges and Ensuring AI Effectiveness
While the benefits of AI in threat detection are compelling, implementing and maintaining these systems is not without its challenges. Overcoming these hurdles is crucial for ensuring the long-term effectiveness and value proposition of AI investments in cybersecurity.
One significant challenge is the ‘black box’ nature of some advanced AI models, where it can be difficult to understand why a particular decision was made. This lack of interpretability can hinder incident response, as security analysts may struggle to fully comprehend the AI’s reasoning.
Addressing Common Obstacles
Proactive strategies can help mitigate many of the challenges associated with AI deployment in cybersecurity, ensuring that the technology delivers on its promise.
- Interpretability and Explainable AI (XAI): Investing in XAI techniques that provide insights into how AI models arrive at their conclusions, fostering trust and aiding human analysts.
- Data Privacy and Security: Implementing robust data governance policies to protect the vast amounts of data processed by AI systems, ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
- Adversarial AI: Developing defensive AI models that can detect and resist adversarial attacks designed to fool or manipulate threat detection systems.
- Resource Allocation: Ensuring adequate computational resources and skilled personnel are available to manage, monitor, and optimise AI systems effectively.
- Vendor Lock-in: Carefully evaluating AI solutions to avoid dependence on a single vendor, promoting interoperability and flexibility.
Continuous research and development in AI cybersecurity are vital to stay ahead of evolving threats and to refine existing solutions. Collaboration between industry, academia, and government agencies can also accelerate the development of more robust and resilient AI-powered defenses.
By proactively addressing these challenges, US organisations can harness the full potential of AI-powered threat detection, transforming their security posture and achieving the projected financial savings while maintaining a resilient and secure digital environment.
The Future of Cybersecurity: AI as a Core Defender
Looking ahead, AI is set to become an indispensable core component of cybersecurity defenses across US networks. Its ability to learn, adapt, and operate at scale positions it as the primary engine for proactive threat detection and automated response. The landscape of cyber warfare will increasingly be defined by the sophistication of AI on both sides of the conflict.
Beyond anomaly detection, AI will play a central role in predictive threat intelligence, vulnerability management, and even automated patch deployment. The goal is to create self-healing networks that can detect and remediate threats with minimal human intervention, allowing security teams to focus on strategic initiatives rather than reactive firefighting.
Evolving AI Capabilities
The continuous development of AI technologies promises even more advanced capabilities for cybersecurity in the near future.
- Predictive Analytics: AI will move beyond detecting current anomalies to predicting future attack vectors based on global threat intelligence and behavioural analysis.
- Autonomous Response: Advanced AI systems will be capable of fully autonomous threat containment and remediation, dramatically reducing incident response times.
- Human-AI Teaming: The synergy between human expertise and AI’s processing power will be optimised, creating highly efficient and effective security operations.
- Threat Hunting Augmentation: AI will proactively identify suspicious behaviours and potential attack paths, guiding human threat hunters to critical areas.
- Adaptive Security Postures: Networks will dynamically adjust their security configurations and policies in real-time based on AI-driven threat assessments.
The integration of AI into every layer of the security stack will create a more resilient and impenetrable defense for US networks. This evolution will not only safeguard critical assets but also contribute to a more stable and secure digital economy.
The future of cybersecurity in the US is intrinsically linked to the advancement and strategic deployment of AI. Organisations that embrace this technology will be best positioned to navigate the complex threat landscape, ensuring operational continuity and financial stability in the digital age.
| Key Aspect | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| Anomaly Detection | AI identifies deviations from normal network behaviour, flagging potential threats early. |
| Financial Savings | Projected 20% reduction in incident response costs for US organisations by 2025. |
| Proactive Defense | Shifts security from reactive to predictive, limiting breach impact and dwell time. |
| Implementation Challenges | Requires addressing data quality, integration, skill gaps, and ethical AI use. |
Frequently Asked Questions about AI Threat Detection
AI systems analyse vast quantities of network data to establish a baseline of normal activity. They then use machine learning algorithms to detect any significant deviations or unusual patterns from this baseline, which could indicate a cyber threat or malicious activity.
AI is projected to save US organisations up to 20% on incident response costs by 2025. These savings come from reducing the duration and scope of breaches, automating initial response actions, lowering false positive rates, and avoiding regulatory fines.
No, AI is designed to augment and empower human analysts, not replace them. AI handles repetitive tasks and sifts through massive data, allowing human experts to focus on complex problem-solving, strategic threat hunting, and making critical decisions.
Key challenges include ensuring high-quality data for training AI models, seamless integration with existing security tools, addressing the cybersecurity skill gap, managing data privacy, and developing explainable AI for better interpretability.
Effectiveness is ensured through continuous monitoring, regular retraining of AI models with new threat intelligence, investing in explainable AI, and fostering collaboration between AI systems and human security teams for optimal performance and adaptation.
Conclusion
The journey towards a more secure digital future for US networks undeniably leads through the strategic adoption of AI-powered threat detection. As cyber threats become increasingly sophisticated, the ability to uncover hidden anomalies with speed and precision is no longer an advantage but a necessity. The projected 20% saving on incident response costs by 2025 underscores the profound financial impact of this technology, transforming cybersecurity from a cost center into a strategic investment. By embracing AI, organisations can build resilient, proactive defenses that protect critical assets, ensure business continuity, and secure their place in the evolving digital landscape.