Deepfake Security Risks: Countering Digital Impersonations

Deepfake security risks necessitate proactive measures for US businesses to effectively identify and counter sophisticated digital impersonations, ensuring operational continuity and protecting sensitive information against evolving cyber threats.
In an era defined by rapid technological advancement, the emergence of deepfake technology presents unprecedented challenges for businesses. Understanding and mitigating deepfake security risks is no longer a futuristic concern but an immediate operational imperative for US businesses navigating a complex digital landscape.
Understanding the Deepfake Threat Landscape for US Businesses
Deepfake technology, leveraging sophisticated artificial intelligence and machine learning, can create highly convincing synthetic media, including audio, video, and images. For US businesses, this technology translates into a new frontier of security threats, from sophisticated phishing attempts to reputational damage and financial fraud.
The ability of deepfakes to mimic individuals, particularly executives or key personnel, makes them a potent weapon for cybercriminals. These digital impersonations can bypass traditional security measures, exploiting trust and human vulnerabilities. Businesses must grasp the nuances of this evolving threat to build effective defence mechanisms.
The Evolution of Deepfake Technology
Early deepfakes were often crude and easily identifiable, but the technology has advanced dramatically. Today’s deepfakes can be incredibly realistic, making detection without specialised tools increasingly difficult. This rapid evolution means that yesterday’s defence strategies may be insufficient for tomorrow’s attacks.
- Improved realism: Advanced AI models generate highly convincing visual and auditory content.
- Accessibility: Tools for creating deepfakes are becoming more user-friendly and widely available.
- Targeted attacks: Deepfakes are now used in highly specific, well-researched impersonation schemes.
Impact on Corporate Security and Trust
The implications of successful deepfake attacks are severe. They can lead to significant financial losses, compromise sensitive data, and erode customer and public trust. A single deepfake incident can have long-lasting repercussions on a company’s brand and market position.
Moreover, deepfakes can be used for corporate espionage, insider threats, and disinformation campaigns, creating a multifaceted challenge for security teams. Recognising these potential impacts is the first step toward developing a comprehensive defence strategy.
In conclusion, the deepfake threat landscape for US businesses is dynamic and complex. It demands a thorough understanding of the technology’s capabilities and its potential to disrupt operations, compromise security, and damage reputation. Proactive engagement with this threat is paramount.
Identifying Deepfake Impersonations: Tools and Techniques
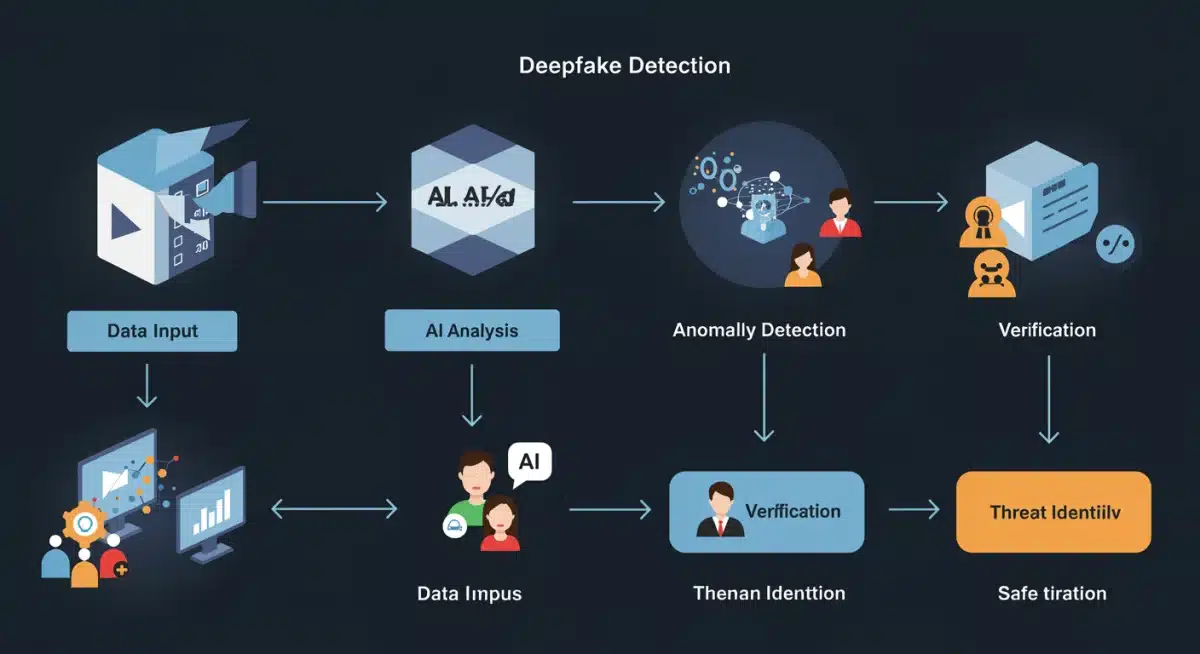
Detecting deepfake impersonations requires a combination of technological solutions and human vigilance. As deepfake technology becomes more sophisticated, so too must the methods employed to identify these deceptive digital creations. US businesses need a multi-layered approach to effectively spot and neutralise these threats.
Reliance solely on visual or auditory cues is no longer sufficient, as advanced deepfakes can fool even trained eyes and ears. Instead, a robust detection strategy integrates AI-powered analysis with forensic techniques and critical human review.
Technological Detection Solutions
Specialised software and AI algorithms are at the forefront of deepfake detection. These tools analyse various digital artefacts and inconsistencies that are often imperceptible to the human eye or ear. Such solutions can process vast amounts of data quickly, flagging potential deepfakes for further investigation.
- AI-powered analysis: Utilises machine learning to identify subtle anomalies in facial expressions, eye blinking, lip synchronisation, and vocal patterns.
- Metadata examination: Scrutinises file metadata for inconsistencies or manipulation indicators.
- Blockchain verification: Explores the use of blockchain to authenticate media origin and integrity.
Human and Forensic Techniques
While technology plays a crucial role, human expertise remains indispensable. Forensic analysts can uncover subtle clues that automated systems might miss, often delving into the minutiae of digital content. Training employees to recognise red flags is also a vital component.
This involves educating staff on common deepfake characteristics, such as unnatural movements, lighting inconsistencies, or unusual speech patterns. Cultivating an environment of scepticism and critical assessment across the organisation strengthens the overall defence posture.
Ultimately, identifying deepfake impersonations is an ongoing battle that requires continuous adaptation. Businesses must invest in both cutting-edge technology and comprehensive employee training to stay ahead of the curve. Combining these elements creates a resilient framework for deepfake detection.
Practical Countermeasures: Strengthening Your Digital Defences
Implementing practical countermeasures is essential for US businesses to fortify their digital defences against deepfake security risks. A reactive stance is no longer viable; instead, a proactive and comprehensive strategy is required to mitigate potential damages. These countermeasures span technological upgrades, policy adjustments, and employee education.
The goal is not just to detect deepfakes, but to prevent their successful deployment and minimise their impact when they do occur. This involves creating a resilient security ecosystem that can withstand sophisticated digital impersonation attempts.
Implementing Robust Verification Protocols
One of the most effective countermeasures is to establish stringent verification protocols for all critical communications and transactions. This moves beyond simple single-factor authentication to more secure, multi-layered approaches that are difficult for deepfakes to circumvent.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA): Essential for accessing sensitive systems and data.
- Out-of-band verification: Confirming critical requests through a different communication channel (e.g., a phone call for an email request).
- Biometric authentication with liveness detection: Using advanced biometrics that can distinguish between a live person and a deepfake.
Employee Training and Awareness Programmes
Human error remains a significant vulnerability. Therefore, comprehensive training programmes are critical to empower employees to recognise and report suspicious activities. Awareness should be a continuous process, reflecting the evolving nature of deepfake threats.
Training should cover not only the technical aspects of deepfakes but also the psychological tactics used by perpetrators. Employees should understand the importance of verifying unusual requests, especially those involving financial transfers or sensitive information. This human firewall is often the first line of defence.
By integrating robust verification protocols with continuous employee education, businesses can significantly strengthen their digital defences against deepfake security risks. These practical countermeasures form the bedrock of a resilient cybersecurity strategy in the age of deepfakes.
The Role of AI and Machine Learning in Deepfake Prevention
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are double-edged swords in the context of deepfakes. While they power the creation of convincing fakes, they also hold the key to their prevention and detection. For US businesses, leveraging advanced AI and ML models is crucial for building next-generation deepfake defence systems.
These technologies offer the ability to analyse vast datasets, identify complex patterns, and adapt to new deepfake techniques more effectively than traditional rule-based systems. Their role extends from real-time detection to predictive threat intelligence.
AI-Powered Detection Systems
AI models can be trained on massive datasets of both real and synthetic media to learn the subtle differences. These systems can then identify anomalies in new content that indicate deepfake manipulation. This includes detecting inconsistencies in facial geometry, speech patterns, and even physiological responses like blinking or breathing.
Such systems operate continuously, providing a dynamic defence against emerging deepfake variants. Their ability to learn and evolve makes them an indispensable part of a modern cybersecurity framework.
Machine Learning for Predictive Threat Intelligence
Beyond detection, machine learning can be used to analyse trends in deepfake attacks and predict future threats. By studying the methods, targets, and motivations behind past deepfake incidents, ML algorithms can help businesses anticipate new attack vectors.
- Pattern recognition: Identifying recurrent deepfake generation techniques.
- Behavioural analytics: Detecting unusual communication patterns that might precede a deepfake attack.
- Risk scoring: Assessing the likelihood of deepfake targeting based on company profile and public exposure.
The symbiotic relationship between AI and deepfake technology means that effective prevention must also be AI-driven. By continuously investing in and deploying advanced AI and machine learning solutions, US businesses can stay a step ahead in the fight against digital impersonation.
Developing an Incident Response Plan for Deepfake Attacks
Even with the most robust preventative measures, deepfake attacks can still occur. Therefore, US businesses must have a well-defined incident response plan specifically tailored to deepfake scenarios. A swift and coordinated response can significantly minimise damage and accelerate recovery.
This plan should outline clear steps for detection, containment, eradication, recovery, and post-incident analysis. It must involve multiple departments, from IT and legal to public relations and human resources.
Key Components of a Deepfake Incident Response Plan
A comprehensive plan addresses not only the technical aspects of an attack but also the broader implications, such as reputational damage and legal liabilities. Each component should be clearly documented and regularly tested.
- Detection and verification: Immediate steps to confirm a deepfake incident.
- Containment strategy: Actions to limit the spread and impact of the deepfake.
- Communication protocol: How to inform internal stakeholders, affected parties, and the public.
- Legal and forensic investigation: Collaborating with legal counsel and cybersecurity experts to gather evidence.
Post-Incident Analysis and Continuous Improvement
After an incident, a thorough post-mortem analysis is crucial. This involves reviewing what happened, why it happened, and how the response could be improved. Lessons learned should be integrated into updated security policies and training programmes.
The deepfake threat landscape is constantly evolving, meaning incident response plans must also be dynamic. Regular drills and simulations help ensure that teams are prepared and protocols remain effective against new deepfake techniques.
In conclusion, a well-structured incident response plan is an indispensable tool for managing deepfake security risks. It provides a roadmap for navigating the chaos of an attack, protecting the business from further harm, and fostering continuous improvement in cybersecurity resilience.
Legal and Ethical Considerations in the Fight Against Deepfakes
The proliferation of deepfakes introduces complex legal and ethical considerations for US businesses. Navigating these challenges requires not only technical solutions but also a keen understanding of evolving legal frameworks, corporate responsibilities, and ethical implications. Businesses must align their defence strategies with these broader societal concerns.
The legal landscape surrounding deepfakes is still developing, but existing laws regarding fraud, defamation, and intellectual property can often apply. Ethical considerations, however, extend beyond legality, touching upon trust, privacy, and the integrity of information.
Evolving Legal Frameworks and Compliance
Several US states and the federal government are beginning to address deepfakes through legislation, particularly concerning their use in political campaigns or fraudulent activities. Businesses must stay abreast of these developments to ensure their policies and response plans are compliant.
Complying with data protection regulations, such as the GDPR or CCPA (even if indirectly impacted), also becomes critical when dealing with deepfake-related data breaches or privacy violations. Legal counsel should be involved in developing deepfake mitigation strategies to ensure adherence to current and future laws.
Ethical Responsibilities and Corporate Governance
Beyond legal compliance, businesses have an ethical responsibility to protect their stakeholders from deepfake harm. This includes transparent communication, investing in robust security, and advocating for responsible AI development.
- Transparency: Clearly communicating the risks and measures taken to protect against deepfakes.
- Stakeholder protection: Prioritising the safety and privacy of employees, customers, and partners.
- Responsible AI: Supporting the development and use of AI in ethical ways that combat misuse.
Addressing the legal and ethical dimensions of deepfakes is not merely about avoiding penalties; it’s about upholding corporate values and maintaining public trust. US businesses that proactively engage with these considerations will be better positioned to navigate the complex future of digital impersonation.
| Key Aspect | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| Threat Identification | Recognising the evolving nature of deepfake technology and its potential for fraud, disinformation, and reputational harm. |
| Detection Strategies | Utilising AI-powered tools and human vigilance to identify subtle anomalies in synthetic media. |
| Proactive Countermeasures | Implementing MFA, out-of-band verification, and comprehensive employee training. |
| Incident Response | Developing a clear plan for detection, containment, communication, and post-incident analysis. |
Frequently Asked Questions About Deepfake Security
Deepfake security risks involve the use of AI-generated synthetic media to impersonate individuals, often for fraudulent purposes. For businesses, this can lead to financial losses through CEO fraud, reputational damage from disinformation campaigns, and compromise of sensitive data via sophisticated phishing attacks.
Detection strategies combine technological tools and human vigilance. AI-powered software can analyse subtle inconsistencies in video and audio. Additionally, employee training to recognise suspicious cues, implementing multi-factor authentication, and out-of-band verification for critical requests are crucial.
Key solutions include robust verification protocols like MFA and out-of-band authentication for sensitive transactions. Comprehensive employee training on deepfake recognition and reporting is also vital. Investing in AI-driven detection systems and having a clear incident response plan are also essential for defence.
AI is a critical tool in fighting deepfakes. While it enables their creation, advanced AI and machine learning models are indispensable for detection. They can identify subtle anomalies in synthetic media, analyse threat patterns, and predict future attack vectors, constantly adapting to new deepfake techniques.
Businesses affected by deepfakes may face legal challenges related to fraud, defamation, and data breaches. Staying informed about evolving state and federal laws regarding deepfakes is crucial. Compliance with data protection regulations and engaging legal counsel for incident response planning are vital steps.
Conclusion
The landscape of digital security is continually reshaped by emerging technologies, and deepfake security risks represent one of the most pressing challenges for US businesses today. Effectively identifying and countering these sophisticated digital impersonations demands a multi-faceted approach, integrating advanced technological solutions with comprehensive human training and robust policy frameworks. By proactively addressing the evolving nature of deepfakes, implementing stringent verification protocols, leveraging AI for detection, and establishing clear incident response plans, businesses can significantly bolster their defences. Ultimately, safeguarding corporate integrity, financial assets, and reputation in the face of these threats requires continuous vigilance, adaptation, and a commitment to fostering a secure digital environment.